Modules
First Module
Information Communication Technology
(ICT)
Information Technology (IT) is a combination of communication, reservation, processing and multimedia capabilities. The main role played by communication networks is called information and communication technology (information technology and communication). An important characteristic of Information technology is that it promotes and facilitates the relationship between human with human, and human with environment due to its changeability and ability to have great impact upon educational, cultural, economic growth, and also globalization,
IT is considered one of the most dynamic majors in science and technology. Today, information and communication technology (ICT) is of first rate in education systems, but the source of this saying is based upon scientific findings particularly training sciences, developmental psychology, and knowledge and education capability. Under the aegis of IT, the inequities and hand can be reduced and educational systems can promote learners’ knowledge and skills; thereby encouraging and improving creativity, critical thinking and learning how to learn.
The most important benefit of ICT in education is the hoped for improvement of learning outcomes. It would provide necessary skilled workforce for the knowledge society while boosting cost/benefit ratio. No less important is the speeding up of the learning process and making it in average much faster than today. Democracy would get to its full potential by democratization of learning, lowering all sorts of boundaries between students and knowledge while bringing knowledge to all students and unlimited number of them. This is already combined with an urban legend that ICT will make learning and teaching much cheaper. Finally, while quality learning does require substantial effort from students and teachers, the process itself could be much easier and more pleasant.
ICT Module Objectives
- Enabling teachers to be more familiar with the new digital-learning tools.
- Improving teachers’ IT skills (storing, retrieving and managing data, using a computer to achieve basic word and data processing tasks, connecting to the internet, using e-mail and web browsing, using search engines …etc.).
- Using ICT for making classroom processes more inclusive and to address multiple learning abilities.
- Dealing independently with a variety of hardware and software and troubleshooting common problems.
- Enhancing learning experiences and providing new sets of skills.
- Learning the basic concepts of distance learning, e-learning and flipped classroom.
- Easy planning and preparation of lessons and designing materials.
- Learning the ways to use ICT tools to make learning process more engaging, innovative and motivating.
Second round of pedagogy, First Module
Third round of pedagogy, First Module
Second Module
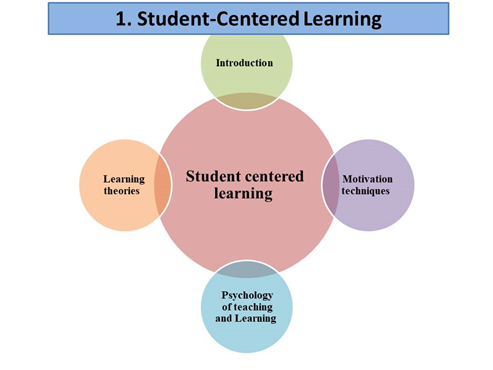
Student-Centred Learning
(SCL)
Module Description
This module deals with the key pedagogical, educational and philosophical dimensions of the student-centred approach with all the major learning theories and contemporary understandings of the processes of learning, teaching and education that have underpinned and enlightened this approach. This module also forms a foundation upon which teachers can build and develop their theoretical and practical pedagogical knowledge, skills and competences that are more essential and compatible with the needs and developments of twenty-first century teaching and education. Lastly, this module provides building blocks that will enable teacher trainees to embark on their journey of becoming effective learning facilitators, guides, mentors and counsellors.
Module Aims & Objectives
This module aims at:
- Developing teacher trainees’ knowledge of the basic learning theories and their relevance to student-centred approach.
- Making teacher trainees aware of the key differences between teacher-centred and student-centred approaches.
- Helping teacher trainees make use of the principles of the learning theories that are consistent with student-centred approach.
- Equipping teacher trainees with pedagogical tools to apply student-centred methods in their teaching.
- Enabling teacher trainees to create different (i.e. physical and virtual) student-centred environments where students need to engage with student-centred learning approaches.
- Making teacher trainees familiar with the psychology of teaching and learning.
Teaching Themes
- Student-centred Approach
- Student-centred learning
- Student-centred teaching
- Learning Theories
- Behaviourism
- Cognitivism
- Constructivism
- Connectivism
- Socio-cultural theory
- Critical theory
- The Psychology of Teaching & Learning
Preliminary Learning Outcomes
Upon the completion of this course, the trainees will be able to:
- Develop a clear understanding of the learning theories and utilise the principles of these theories that are more aligned with student-centred approach.
- Develop a pedagogical mindset or identity that allow students to exercise greater learning autonomy.
- Create both physical and virtual learning environments to be primarily student-centred through making use of different student-centred teaching methods.
- Apply student-centred pedagogy to support and facilitate the learning journey of their students.
- Understand the importance of psychology to the processes of teaching and learning.
Second round of pedagogy, Second Module
Third round of pedagogy, Second Module
Third Module
Innovative Pedagogical Approaches, Assessment and Creating Learning Environments
Introduction
This module attends to three themes that form the main components of the teaching-learning process, namely Innovative Pedagogical Approaches, Assessment and Creating Learning Environments.
Teachers’ effective knowledge and right handling of these themes can noticeably result in learners’ (1) better understanding and (2) retaining of the materials taught and duly (3) bringing about the set objectives.
The theme “Innovative Pedagogical Approaches” tackles a set of varied teaching techniques, activities and applications which a teacher can either adopt or adapt so as to (1) account for learners’ different educational backgrounds and cognitive, affective and behavioral levels and (2) contribute to better learning outcomes.
As for the theme “Assessment”, it is widely acknowledged that assessment helps in pinpointing the challenging areas in learners’ performance. Additionally, teachers’ understanding, application and use of the proper assessment tools would be quite beneficial in terms of
(1) attracting learners’ attention to the areas of strength and weakness in their performance, and
(2) providing them with the feedback required to enhance their learning so as to bring about the set objectives feasibly and fruitfully.
Learning Outcomes
On the completion of this theme, participants are expected to be able to
- align the assessment tool with the learning outcome of the course,
- ensure the validity of the assessment tool,
- design different forms of formative, diagnostic and summative assessments,
- know tools used for assessing knowledge, skills and attitude,
- develop reflection and self-assessment, and
-. assess students’ deep learning through authentic, project or problem based assessment.
Concerning this module, participants studying this module are expected to know about the following assessment tools:
- Self-Assessment, Peer Assessment, Observation of Daily Activities, Written Examinations, and Case Studies.
Finally, the theme “Creating Learning Environments” tackles the academic, social and psychological aspects of the teaching-learning process. Learners’ preparedness to be engaged in the learning activities can be brought about when learners feel
(1) they are not working under any type of pressure,
(2) their needs and set objectives are well realized by teachers,
(3) their collaboration can effectively facilitate, guide and scaffold better learning, and
(4) teachers are real sources of assistance and guidance.
Second round of pedagogy, Third Module
Third round of pedagogy, Third Module
Fourth Module
Research & Development
(R & D)
Research is the systematic approach to obtaining and confirming new and reliable knowledge”. This is a general definition which applies to all disciplines. To be more specific, research is
- Searching for explanation of events, phenomena, relationships and causes. What, how and why things occur. Are there interactions?
- A process that is planned and managed to make the information generated credible. The process is creative and circular and always leads to more questions.
Research design
There are several types of research designs. A researcher selects a particular type of research based on the nature of his/her study. Each type of research has its advantages and disadvantages.
Descriptive Designs
These are designs that describe phenomena in order to answer a research question. They are mainly used in case of quantitative research, but may also be sometimes used in qualitative study. Quantitative descriptive designs produce very weak ‘evidence’ in comparison to experiments but are useful in knowing in-depth information about the subject matter. They can be of the following many types::
- Descriptive research.
- Naturalistic observation.
- Case study.
- Cor-relational studies:
- Case control study.
- Cross sectional study.
- Longitudinal study.
- Cohort study.
- Observational study.
- Semi-experimental designs.
- Quasi-experimental design.
- Field experiment.
- Twin studies.
- Experimental designs.
- Double-blind experiment.
- True experimental design.
Second round of pedagogy, Fourth Module
Third round of pedagogy, Fourth Module
fifth Module
Competency-Based Education
(CBE)
Competence is a combination of knowledge, skills and attitudes appropriate to the context. Knowledge and skills are components, attitude joins them together.
Principles of CBE
- Recognizing prior learning and learning outside the course.
- Self-paced Programme : Learners take as much or as little time as they need to
understand the material.
- Shifting attention from grades to learning.
Competence Based Curriculum
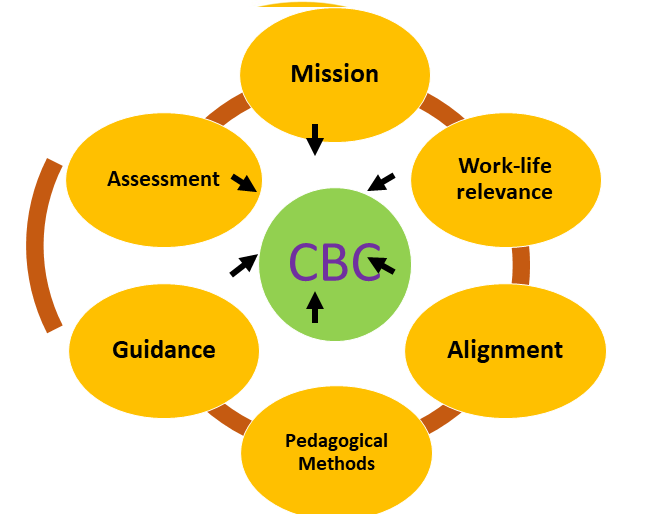
How to Design CB Curriculum?
- Answering the needs of local area. External stakeholders to be involved in such a way universities justify their Existence.
- The curriculum should disclose what a student is capable of doing.
- Alignment of Curriculum: means its competences, learning activities and pedagogical methods and assessment tools should be aligned.
- The skills and expertise are acknowledged in teaching and supervision methods.
- Student Guidance: Support the students in selecting the competences to build a career.
- Assessment criteria are based on learning outcome and help students to reflect upon their competences.
Second round of pedagogy, Fifth Module
Sixth Module
EduPreneurship & University Working Environment
What is Entrepreneurship Education?
Based on the Finnish understanding, Entrepreneurship education is the combination of enterprise and entrepreneurship education. Therefore, the definition varies based on the country. Some countries have provided national definition for the term such as France, Finland, Netherlands, Malta, Spain and United Kingdom. However, the common understanding used by the European Union encompasses dual focus. The first focus relates to the development of entrepreneurial skills, attitude and knowledge that assists individuals to shift ideas into action. The second focus explains entrepreneurship in wider scope other than the sole business and economic activities, but entrepreneurship encompasses a wider range of filed. Based on that understanding, the Union provided a common definition for entrepreneurship education which refers to the development of skills, knowledge and mind-set for the purpose of turning ideas into entrepreneurial action.
Teachers here should be able to develop individual key competencies to encourage active citizenship, employability, public participation, personal development and individual autonomy. These competencies are keys to personal development and relevant across the lifelong learning in all fields and forms of learning, education and training.
The concept of entrepreneurship education includes student centred learning in competence based education that leads to value creation in authentic learning environment. In the other words, entrepreneurship education activates students and facilitate methods to transfer their knowledge, skills and attitudes into action. In such cases students become critical in their thinking and creative in their work. Students’ knowledge, skills and mind-set is developed through entrepreneurship education that leads to idea generation and transfers students’ ideas into action. Teachers are playing a key role here to facilitate learning environment that helps students to be creative in their own way. Entrepreneurship can also be described as the visualization, realization and operationalization of new ideas by the individuals who are capable of utilizing available information and resources for the implementation. Entrepreneurs are usually visualize their ideas and combine different dimensions of entrepreneurship as autonomy, innovation, reactiveness, risk taking, competitive aggressiveness and intellectual capital into holistic realities to create something new. The learning environment and education institution are playing a major role in facilitating the entire process by helping students and encouraging them to be active citizen and creative.
Learning outcomes
- Teacher students become critical thinker and transfer that knowledge to their students.
- Teacher students will be taught how to become different and creative person and transfer that knowledge to their students.
- Teacher students will be able to empower students to tackle opportunities.
- Teacher students will be able to initiate ideas and transfer that knowledge to their students.
- Teacher students will be able to become collaborative and understand the importance of team work at workplace and transfer that knowledge to their students.
- Teacher students will be enriched with problem solving skills and transfer that knowledge to their students.
- Teacher students will be able to convert learning to new and different situations and career success.
- Teacher students will understand the current economic changes and find out their ways to redesign teaching methods accordingly.
- Teacher students will be able to know how to organize curriculum to support new economic realities, technological development and deeper learning outcome.
- Teachers will be able to prepare students to the project based world to obtain high levels of expertise overtime.
University-Work Environment
University- Work Environment Cooperation means that different forms of cooperation and knowledge transfer between universities on the one side, and companies and businesses on the other. During the teaching of this this module the focus will be on the role of education in knowledge transfer and the development of knowledge through models suitable for institutions of higher education. These should result in benefits for both sides: in improved products, services and processes for companies and in improved competitiveness, relevance and visibility for institutions of higher education.
Higher education should give a person an opportunity to succeed in today’s global economy. Modern universities provide their students with various programmes aimed at preparing them for different economic sectors, helping them to stay and progress in the labour market for long, programmes that make a difference for labour market outcomes and keep pace with changes in the global economy and changes in the innovation process. Universities promote lifelong learning; they offer opportunities to engage and attract professionals into training and professional development.
Proposed Themes of the Module
- Career Guidance and Counselling.
- Apprenticeship.
- University Societal Role.
Second round of pedagogy, Sixth Module
